
What is testosterone?
Testosterone is a steroid hormone, part of the group of sex hormones referred to as androgens. Testosterone is the primary male hormone and is required for the development of male sex organs and maintaining secondary male sex characteristics such as muscle mass growth, bone density and fat mass distribution. Testosterone is produced mainly in the testicles and adrenal glands.
Testosterone functions
Testosterone has many essential functions in the body. The main functions are:
- Muscle growth and healthy bone density: Testosterone enhances protein synthesis, leading to more rapid muscle growth. It also increases bone density, helping to prevent osteoporosis.
- Behaviour effect: Testosterone affects gender behaviour including sex behaviour. It also affects mood and can contribute to a sense of well-being.
- Sexual function and fertility: Testosterone increases libido (sex drive) and supports erectile function. It also affects sperm quality and therefore fertility.
- Metabolism: It affects metabolism, for example it regulates glucose and lipid levels in the blood, supporting healthy weight.
- Blood cell production: Testosterone stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells. This
is also important to help prevent anemia.
Testosterone levels change with age and lifestyle
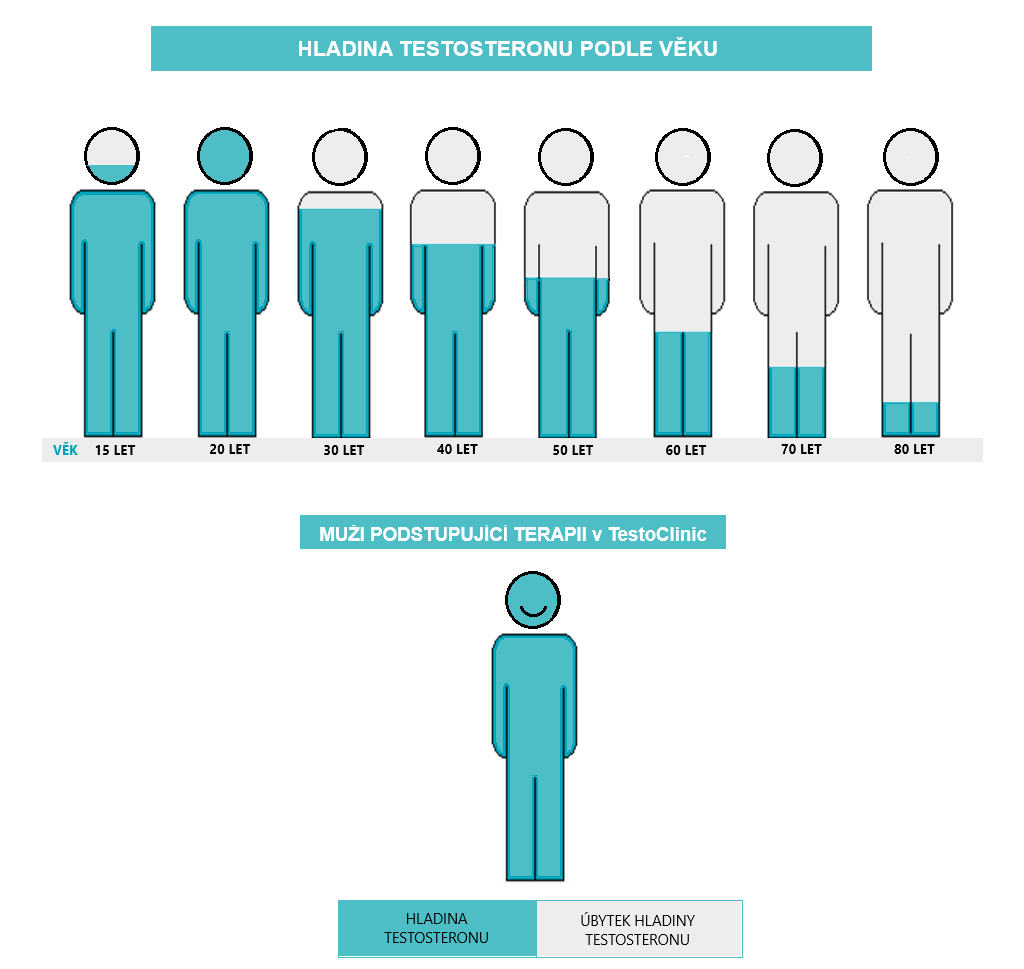 During a man’s lifetime, testosterone levels are usually highest between 20 – 30 years of age in young healthy men. At this time men are normally at their sexual and physical peak.
During a man’s lifetime, testosterone levels are usually highest between 20 – 30 years of age in young healthy men. At this time men are normally at their sexual and physical peak.
Testosterone levels usually start to decline after the age of 30. This decrease is natural and means generally a drop of about 1% per year. Nonetheless the decrease is always unique to an individual and some men notice a significant decrease, whilst others have a much slower decrease.
The decrease of testosterone with age is also known as andropause or male menopausal syndrome. It can lead to changes such as decreased libido, loss of energy, loss of muscle mass, increase in body fat mass, and it may also contribute to emotional and cognitive changes. It is important to note that healthy life style, healthy diet and regular exercise can help ease some of these negative effects of lower testosterone levels.
We understand that this is, for many men, a sensitive topic but it is crucial that men are aware of these changes and feel safe to discuss their options with a doctor who can recommend suitable steps in order to maintain health and vitality, even at an older age.
Low testosterone levels can lead to many health problems, such as muscle mass loss, an increase in body fat, lower bone density, tiredness, low libido and depression. On the other hand very high levels may cause negative side effects such as increased aggressiveness, acne or risk of heart disease. It is recommended to consult with a medical expert on how to optimise testosterone levels. Only medical experts can monitor all negative aspects in relation to the client’s health and create a suitable therapy minimising any potential risks for the client.